11.1 What Is A Volcano? Physical Geology, First University of
noun volcano that has had a recorded eruption since the last glacial period, about 10,000 years ago. dormant volcano noun volcano that has erupted in the past but is unlikely to erupt soon. erupt verb to explode or suddenly eject material. lava noun molten rock, or magma, that erupts from volcanoes or fissures in the Earth's surface. magma
St Margaret's Academy Geography Blog Year 9
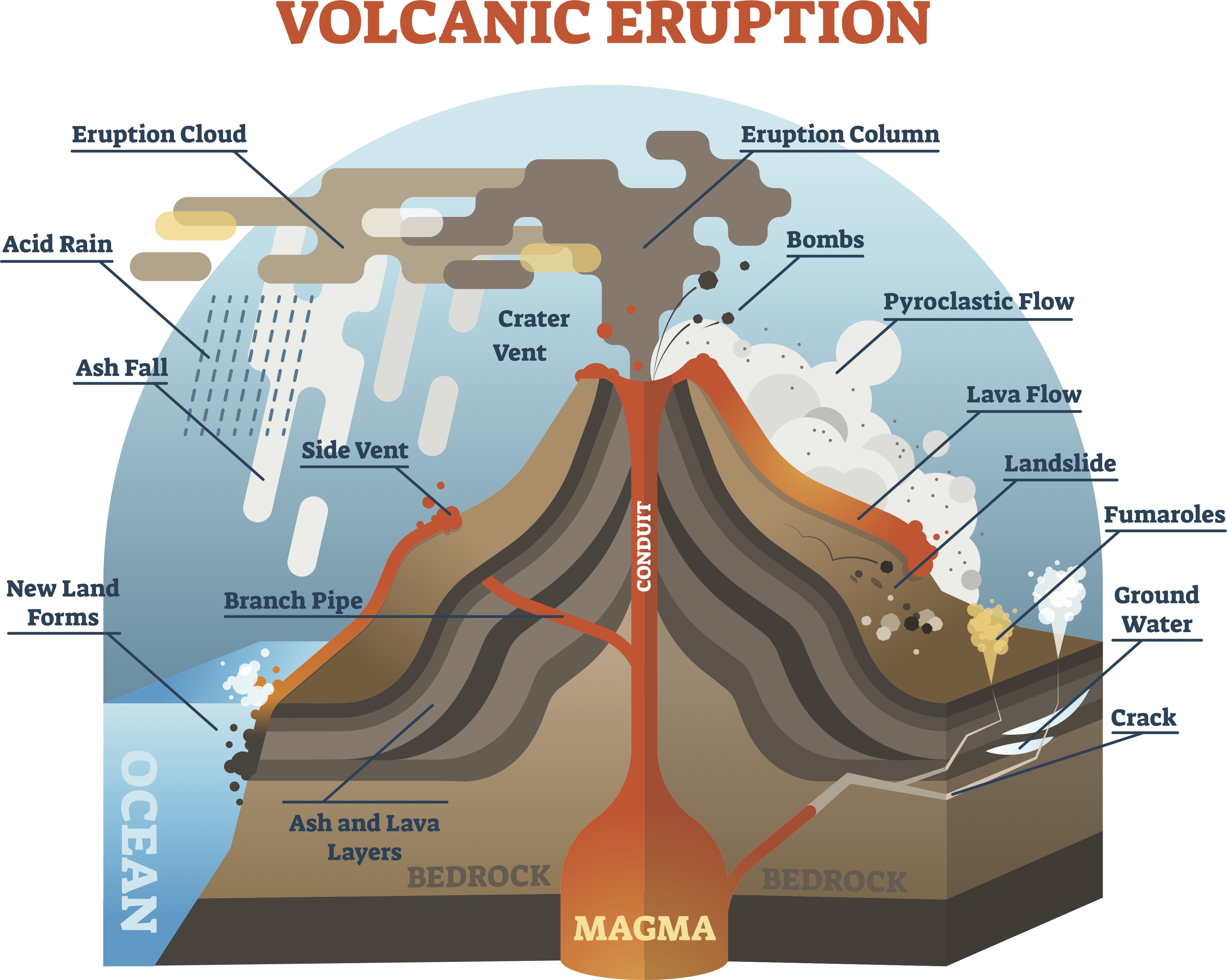
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): General diagram of volcanic hazards. While the most obvious volcanic hazard is lava, the dangers posed by volcanoes go far beyond lava flows. For example, on May 18, 1980, Mount Saint Helens (Washington, United States) erupted with an explosion and landslide that removed the upper 400 m (1,300 ft) of the mountain.

ENG 001 Language & Writing Blog Post 2 Diagrams
Learn how to classify rocks Although volcanoes are often seen as being destructive they are also constructive. They add more land to the surface of the Earth and, when weathered, provide us with a nutrient-rich soil for agriculture.

8 Images Diagram Of A Volcano For Kids And View Alqu Blog
A volcano is an opening in Earth 's crust. When a volcano erupts, hot gases and melted rock from deep within Earth find their way up to the surface. This material may flow slowly out of a fissure, or crack, in the ground, or it may explode suddenly into the air. Volcanic eruptions may be very destructive. But they also create new landforms.
Volcano Diagram Free Images at vector clip art online
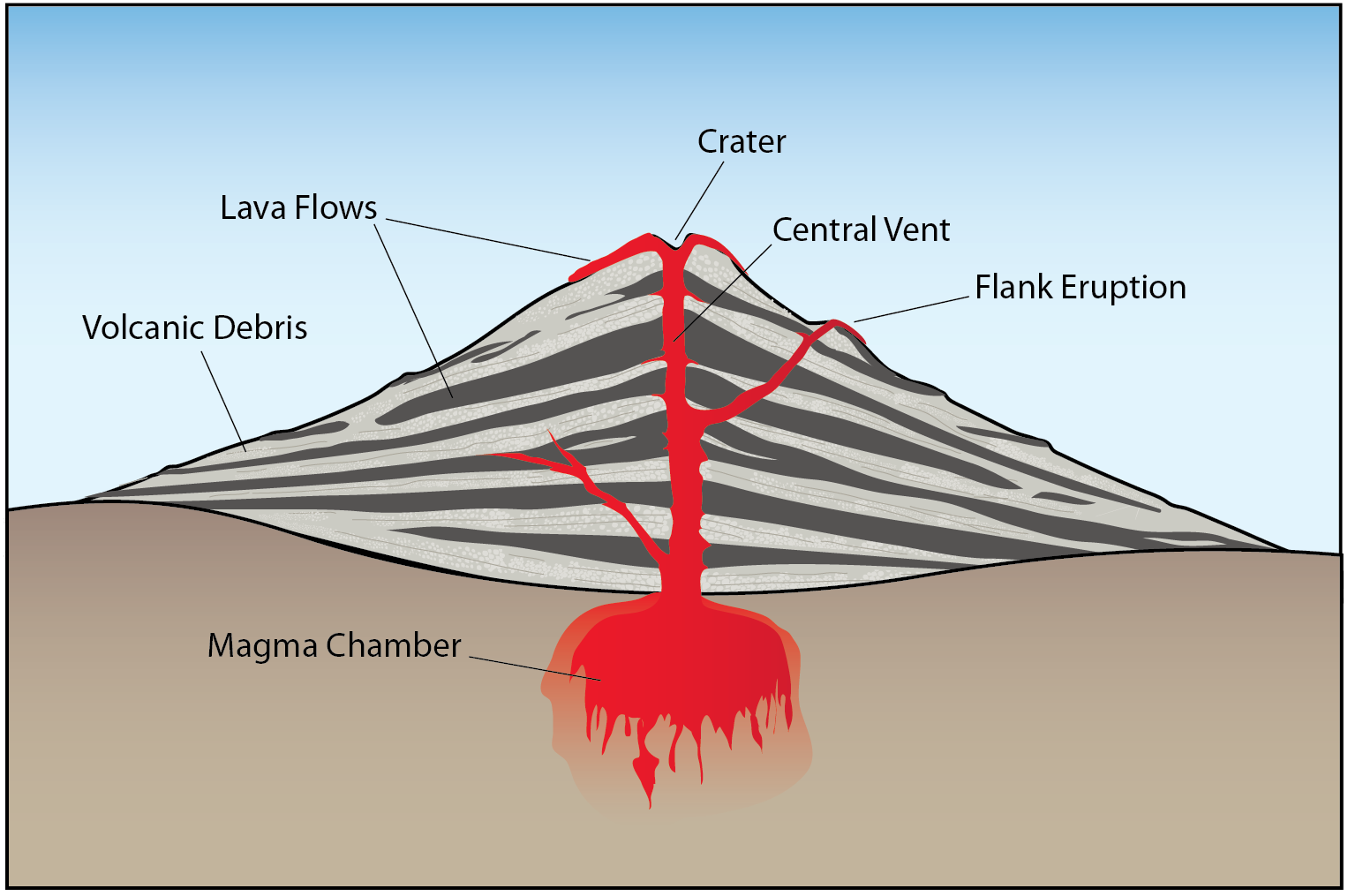
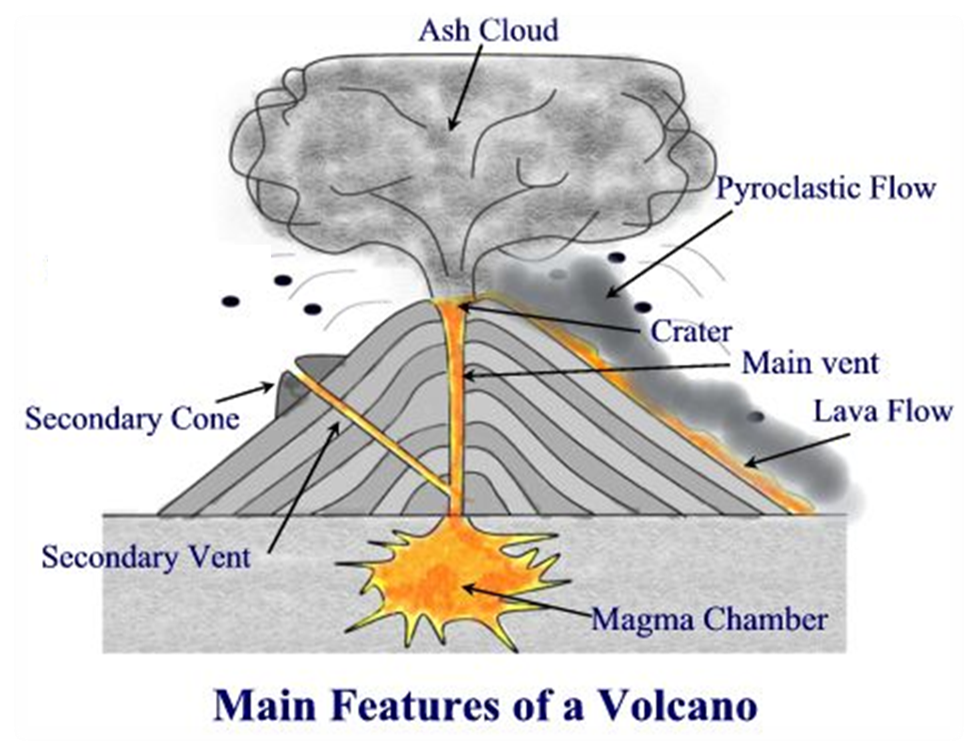
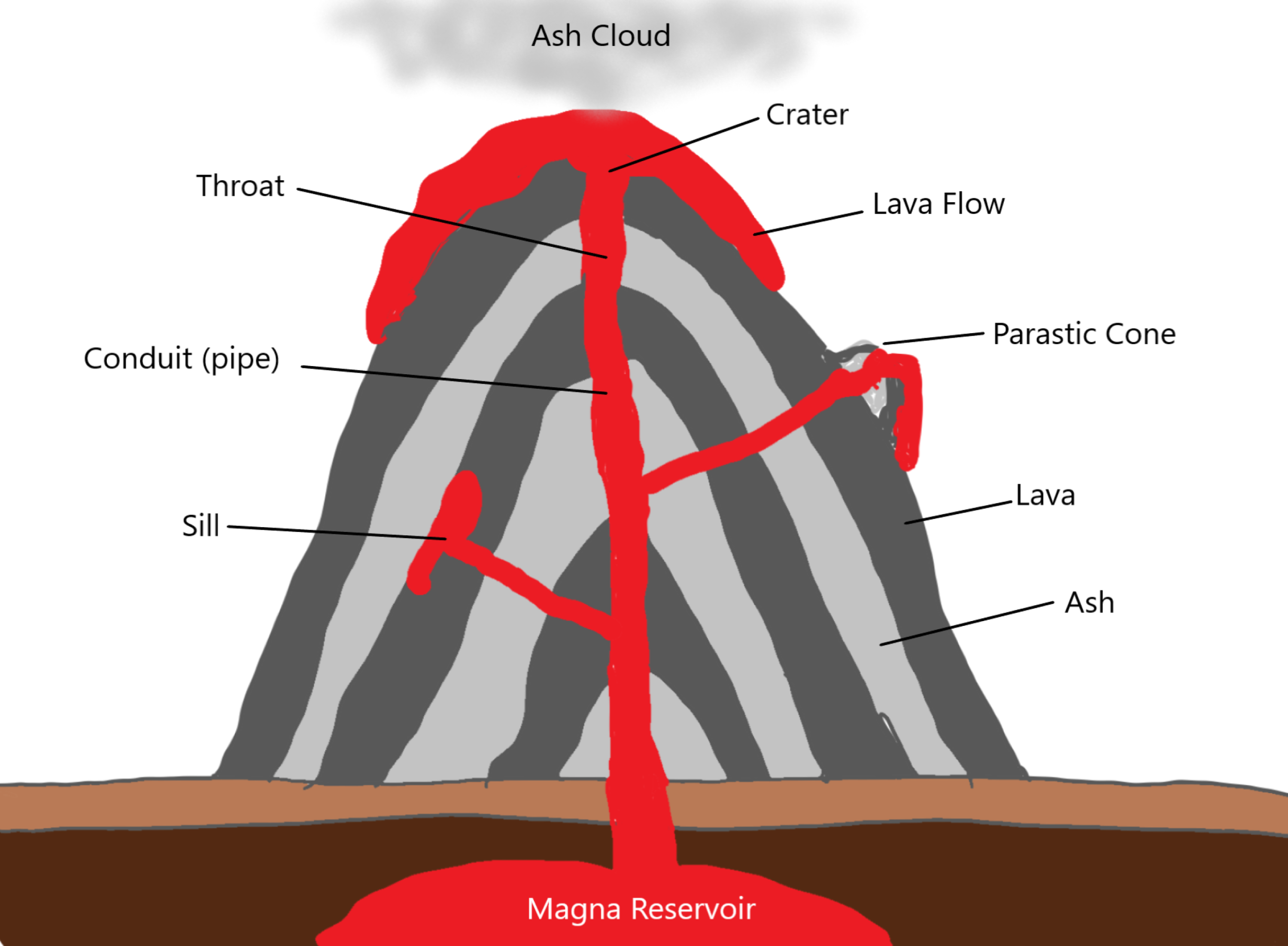
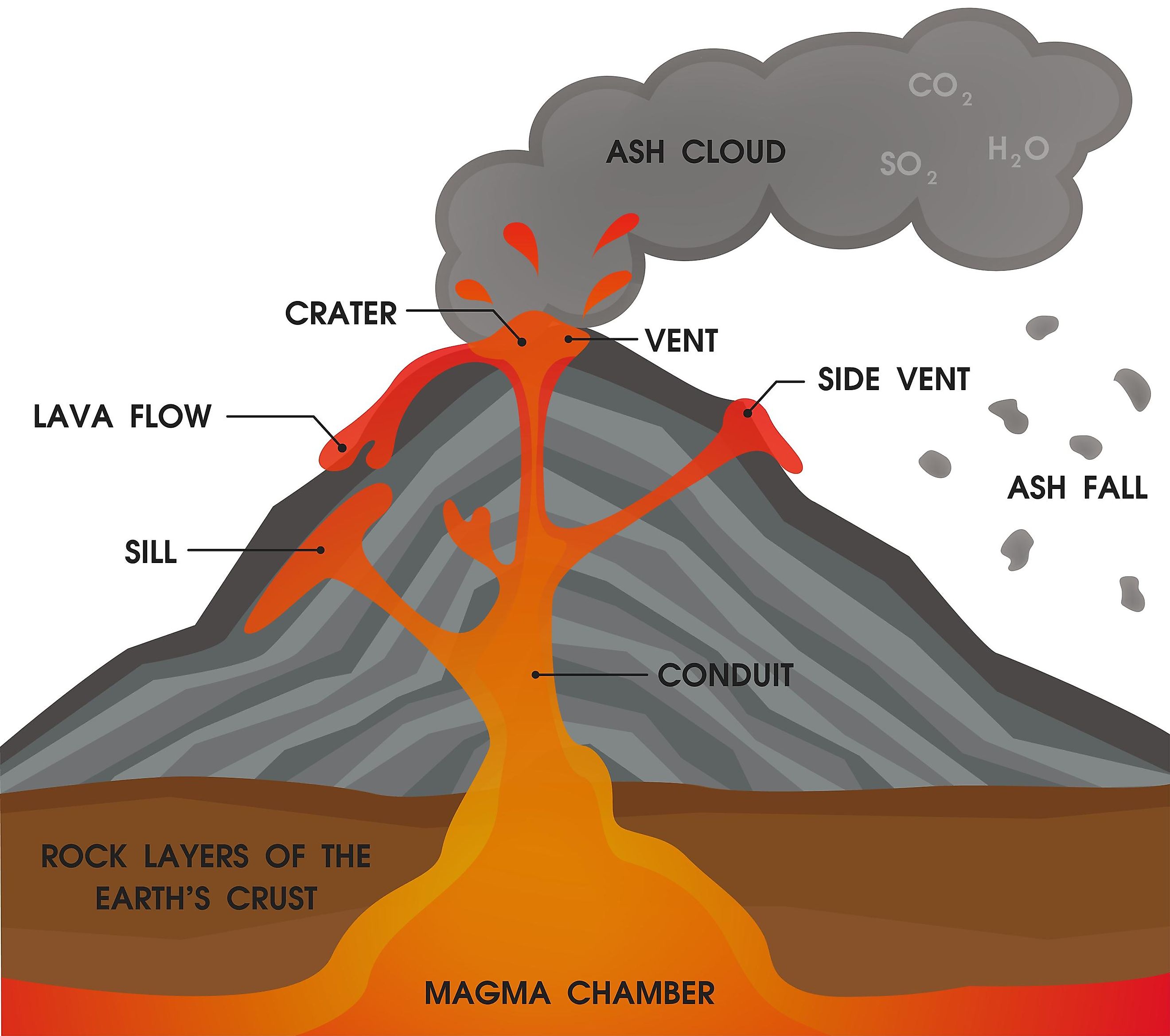
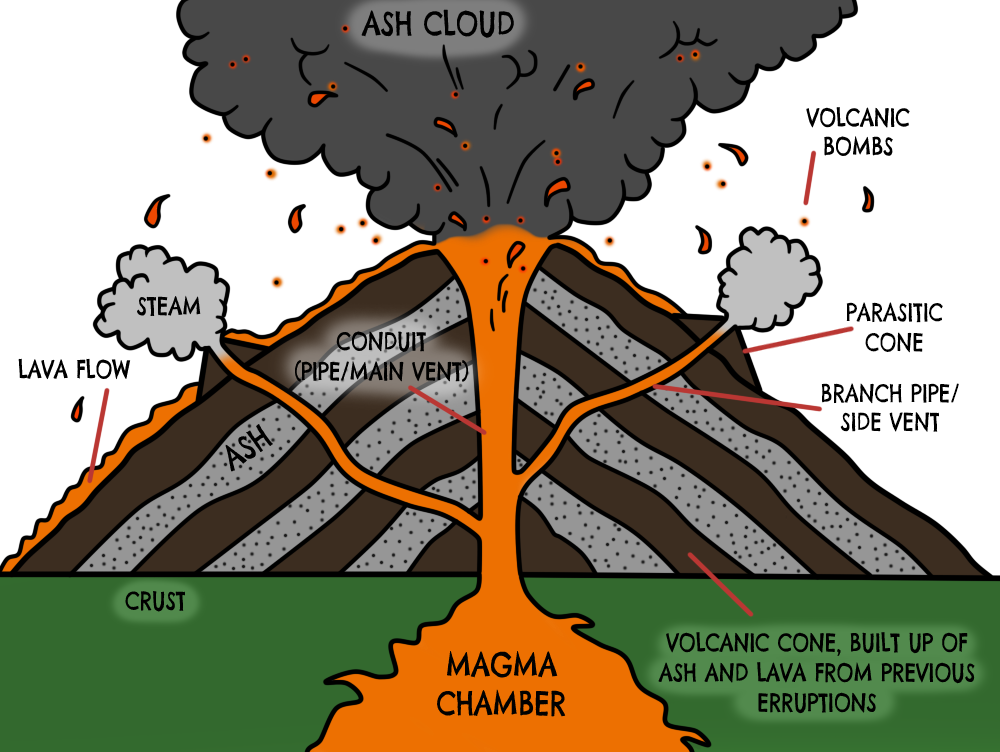
Aside from the "volcanic cone" (i.e. the cone-shaped mountain), a volcano has many different parts and layers, most of which are located within the mountainous region or deep within the Earth.

Volcanoes Weather Wiz Kids
Jose Juan Gutierrez Updated: Dec 28, 2023 3:38 PM EST What Is a Volcano? A volcano is a geological rupture in the earth's crust triggered by pressure, temperature, and other natural forces in the planet's interior. These forces drive gasses and hot liquid known as magma out through a volcano's orifice, which is referred to as a "vent."
Why Do Volcanoes Erupt? WorldAtlas
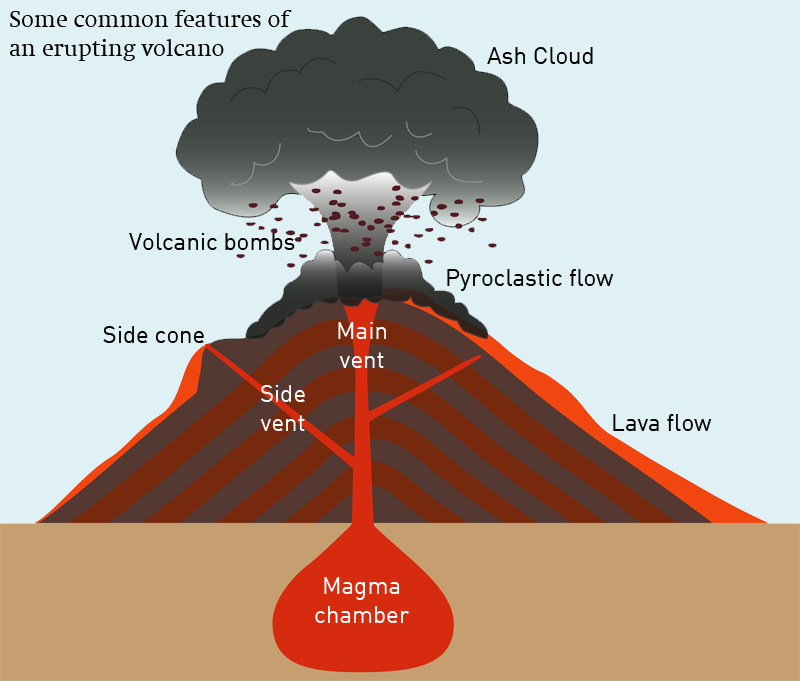
Volcanoes have distinctive features: magma chamber - this is where the molten rock is stored beneath the ground main vent - this is the channel through which magma travels to reach the Earth's.
Volcanodiagram by TJackification on DeviantArt
Diagram with feature labels. Credit: NPS illustration by Trista Thornberry-Ehrlich (Colorado State University). Glossary—Cinder Cone Volcanoes Ash Cinder

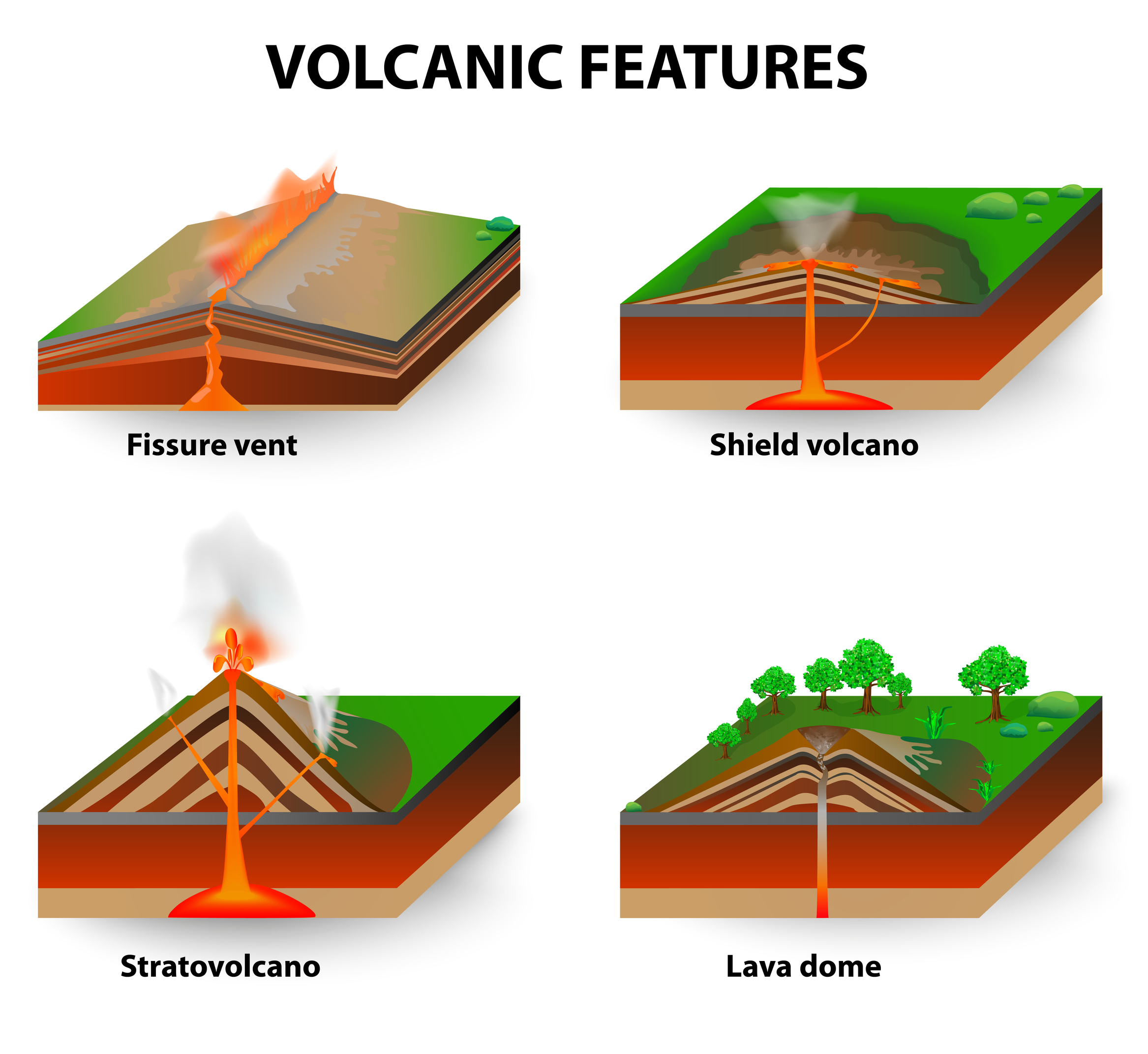
Major forms of extrusive activity types of volcanoes. Shield
5. Lava Dome. Lava domes are fascinating geological features that can grow over time as layers of lava accumulate. They often pose potential hazards due to their instability and the potential for explosive eruptions when pressure builds beneath them.
Types of Volcanoes
What's the difference between lava and magma? What are volcanic vents, dikes, and fissures? In this anatomy of a volcano, explore the basic geological features of a volcano such as Mt. St..
What are lahars and pyroclastic flows? Geography
Diagram showing the inside of a volcano | Eschooltoday Inside a volcano The diagram representation above shows what a basic volcano looks like. How does the inside of a volcano look like? The magma chamber: This is the area with a massive collection of magma below the earth's crust from which magma flows out. Crater:

VOLCANO DIAGRAM Unmasa Dalha
The main types and features of volcanoes; The main features of earthquakes; Distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes;. Volcano Interactive Diagram. Share this: Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window) Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Shetland's volcano Shetland Amenity Trust
This simple schematic diagram shows the movement of the tectonic plate (light brown) over a mantle plume, or hot spot, to produce a chain of volcanic islands. The superheated magma rises through the mantle (yellow), melts the crust above (brown) and flows on to the surface forming a volcano.

Diagrams Of Composite Volcanoes
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
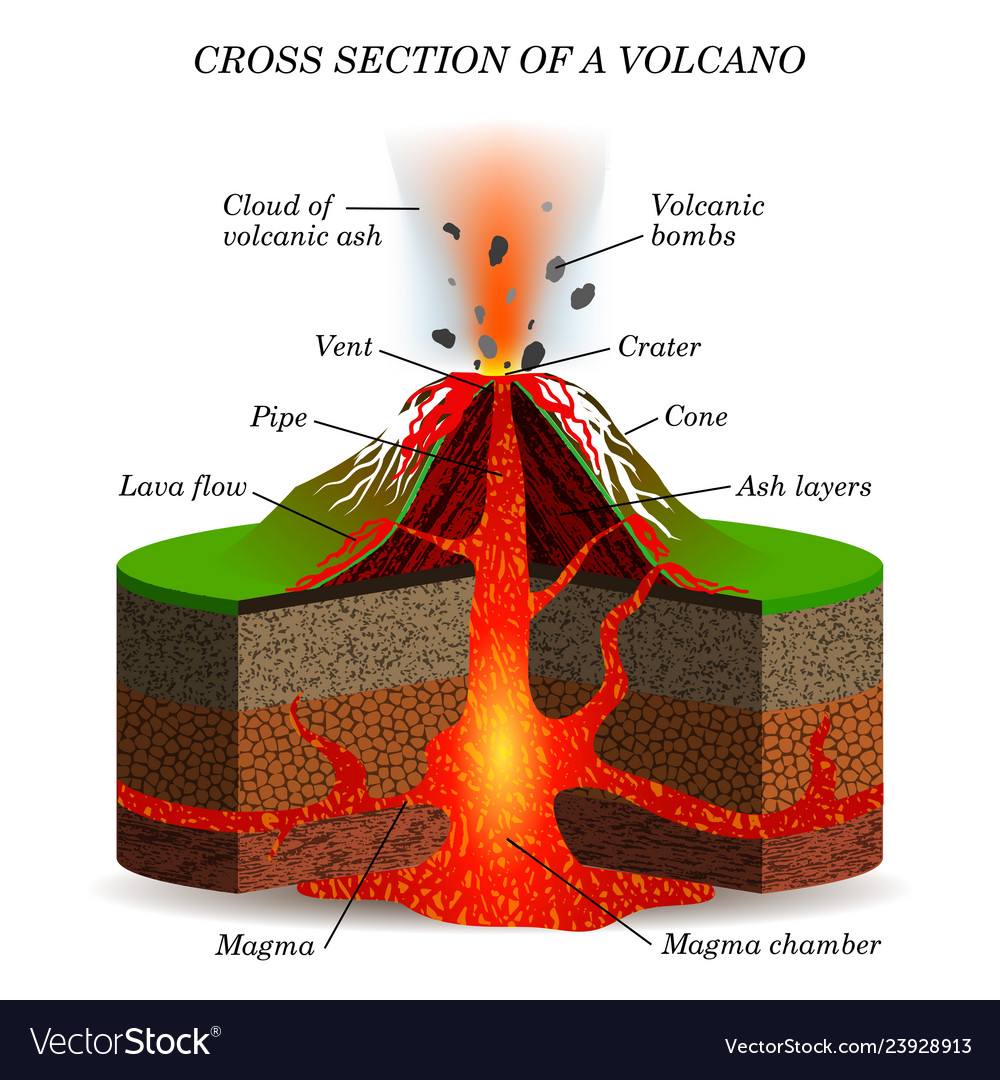
Volcano igneous eruption in the cross section Vector Image
A volcano is an opening in the earth's crust through which magma, ash and gas erupt. Volcanoes can be different shapes although they are commonly cone shaped mountains as seen in this picture. These cone shaped volcanoes are made up of layers of ash and lava. Most volcanoes are found at plate boundaries. Mount Fuji, Japan Mount Fuji in Japan.

Types of Volcanoes
A volcano is a place on the Earth's surface (or any other planet's or moon's surface) where molten rock, gases and pyroclastic debris erupt through the earth's crust. Volcanoes vary quite a bit in their structure - some are cracks in the earth's crust where lava erupts, and some are domes, shields, or mountain-like structures with a crater at the summit.