
Social Structure Medieval Japan
1. Emperor The Emperor is considered the highest position in Japanese society. Although the Emperor no longer holds political power, they are a symbol of the nations unity and continuity. 2. Nobility and Aristocracy Traditionally, the noble class held considerable influence and wealth.
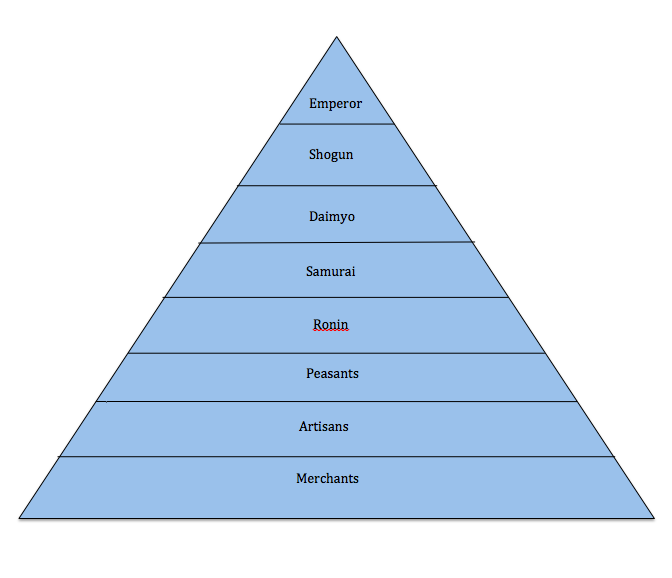
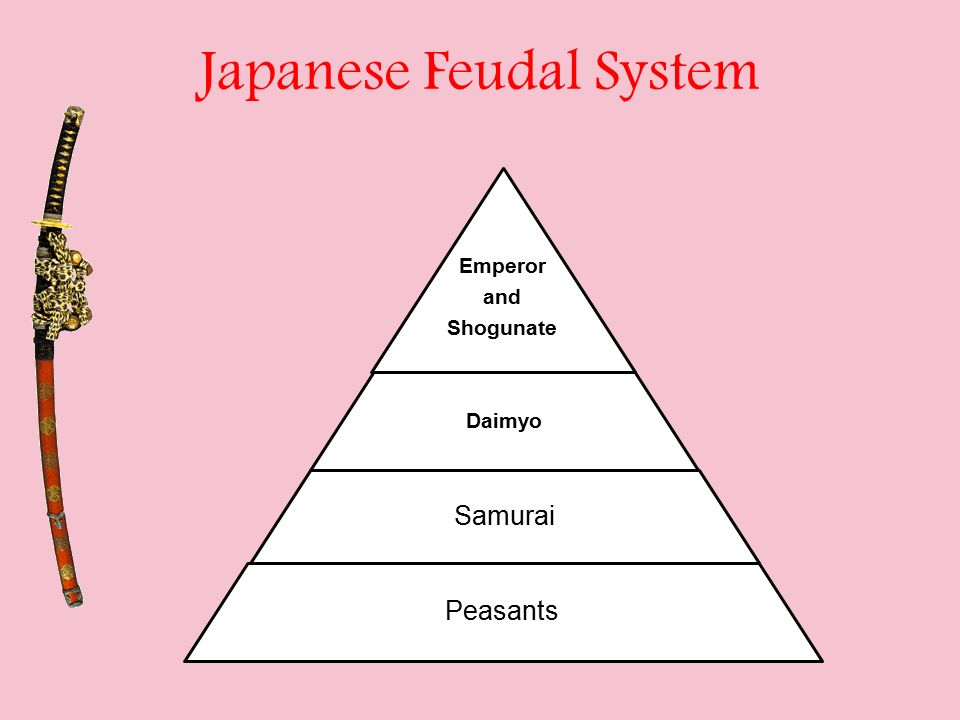
Hierarchy of Japanese feudal society
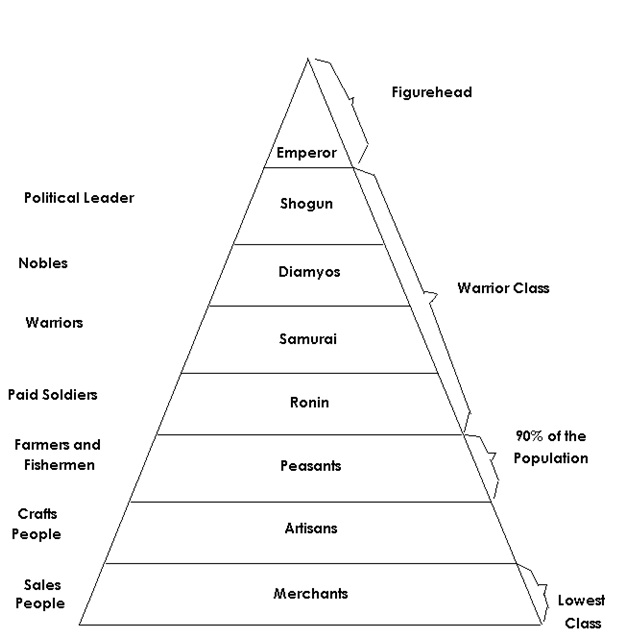
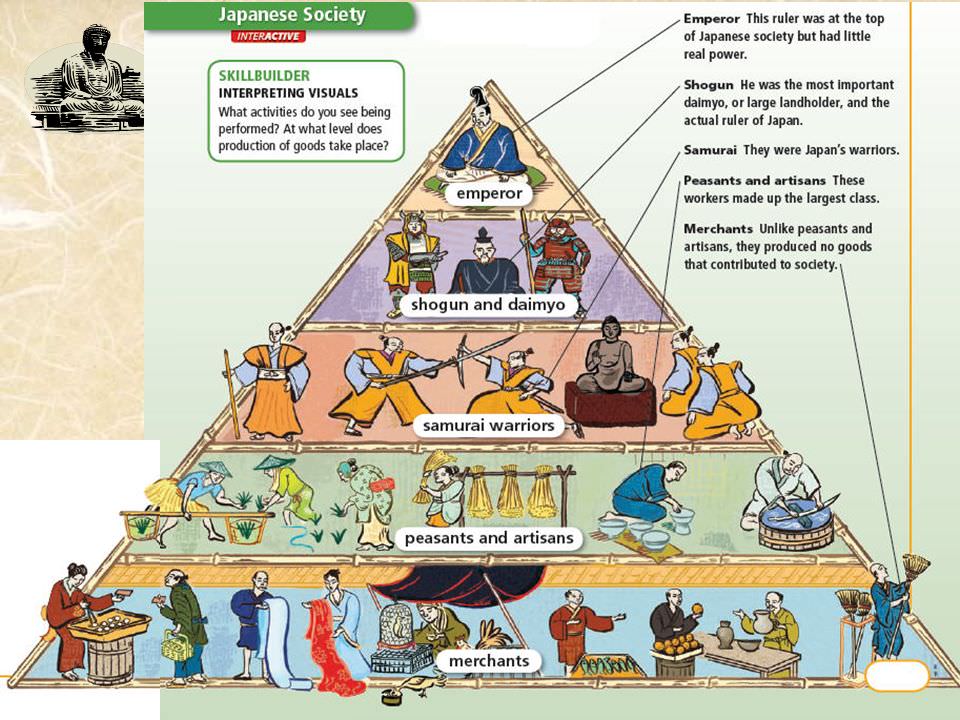
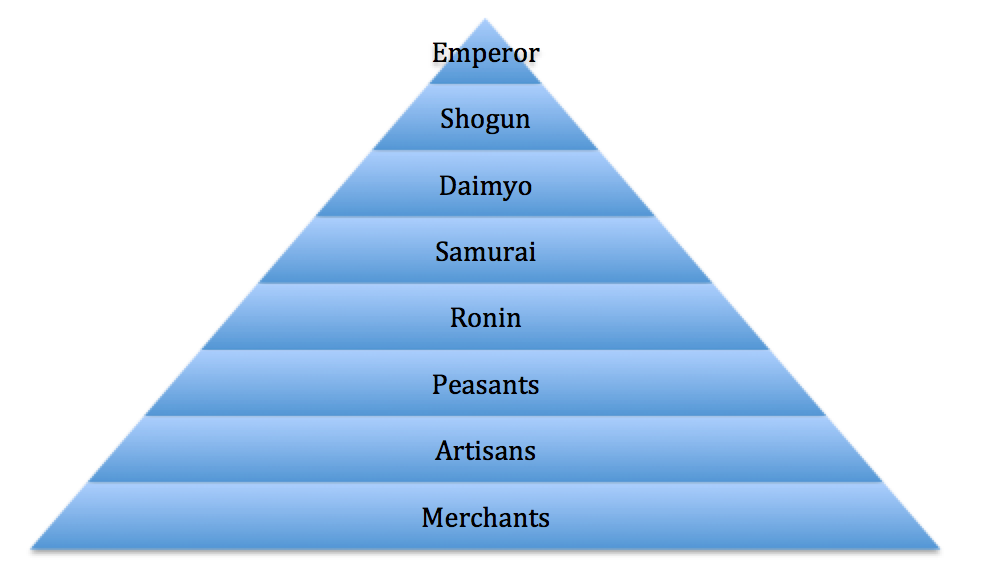
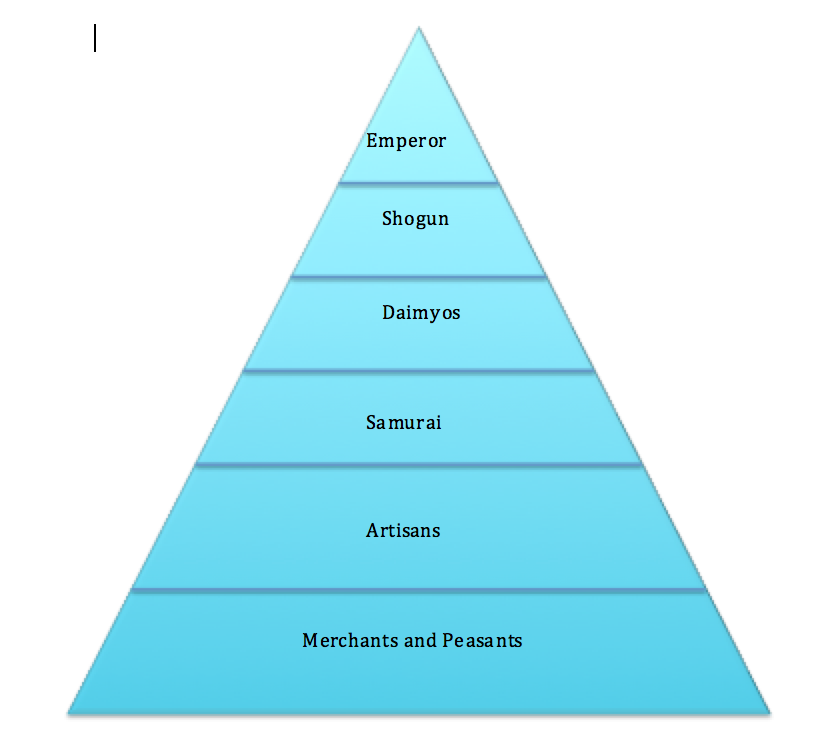
Feudal Japan had a four-tiered social structure based on the principle of military preparedness. At the top were the daimyo and their samurai retainers. Three varieties of commoners stood below the samurai: farmers, craftsmen, and merchants. Other people were excluded entirely from the hierarchy, and assigned to unpleasant or unclean duties such as leather tanning, butchering animals and.

Hierarchy Japan Under the Shoguns
Japanese social hierarchy portrays a systematic classification of all the social classes in the Japanese social society. This hierarchy is quite different from the social system that was employed in the ancient Japan as since the ancient times society has undergone several structural changes.
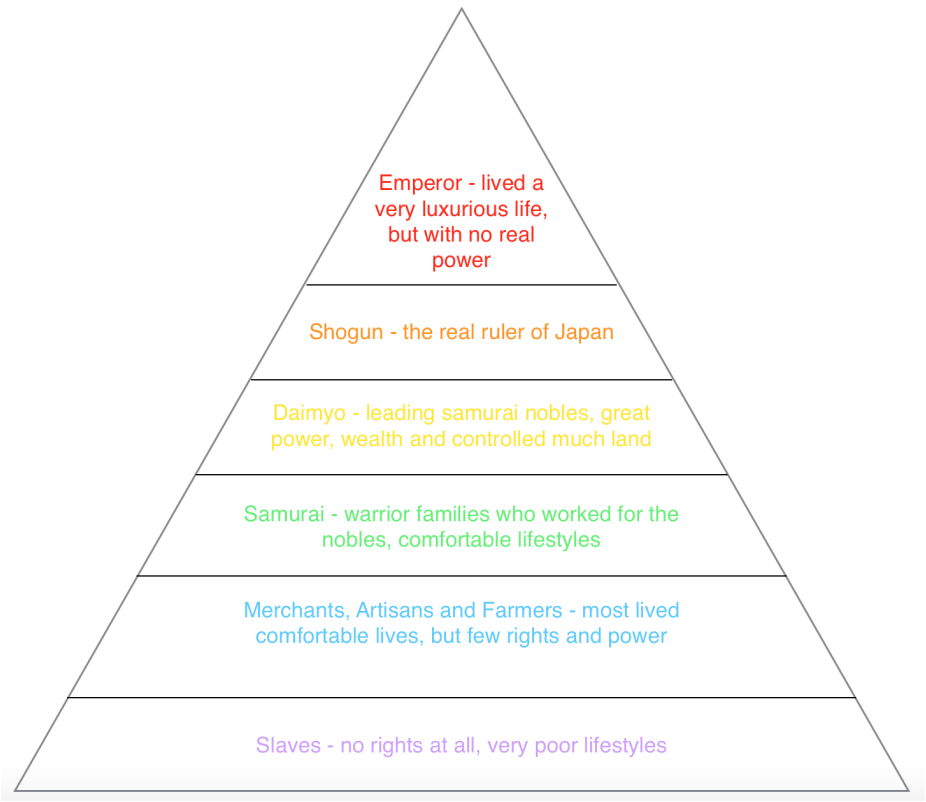
Feudal System Pyramid Shogunate Japan by Britta Hughes
Share One aspect of Japanese corporate culture that often is difficult for non-Japanese to understand is the importance of hierarchy. The status relationships among various different members of the organization is a key determining factor in how they interact with each other, and how they expect others to interact with them.
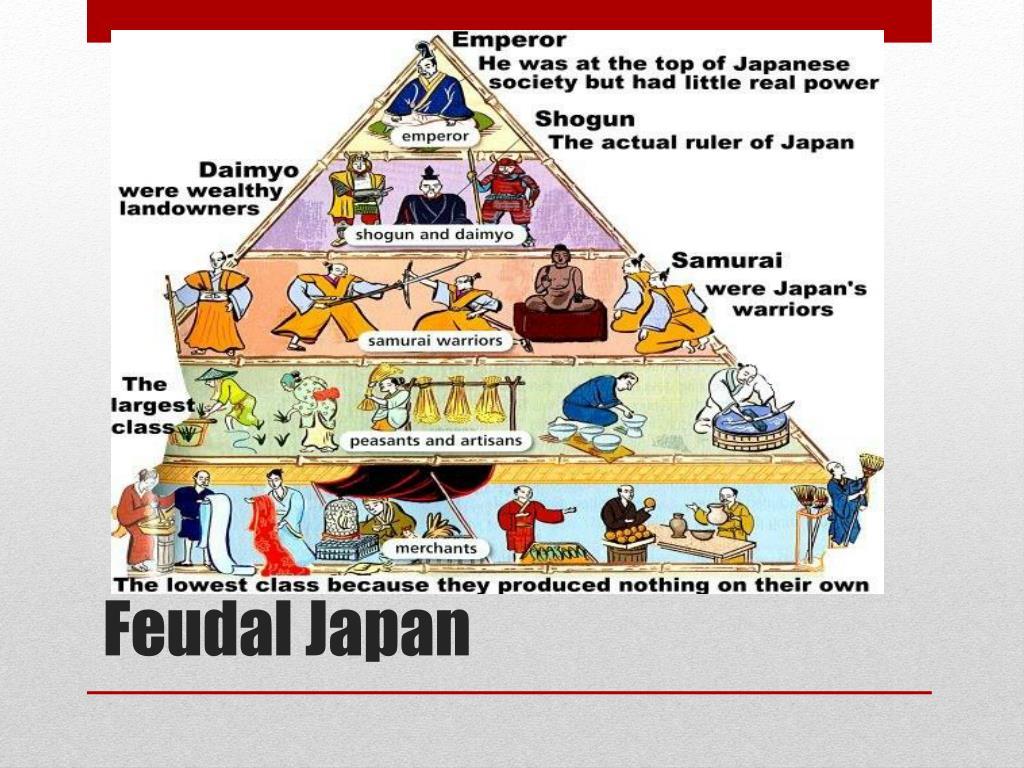
PPT Feudal Japanese Society PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2241313
Hierarchy of Japanese Feudal Military. The Japanese society witnessed various form of classification on the basis of different factors. One such way of segregating the society was the feudal system. Japanese Feudal Military hierarchy portrays the classification of Japanese military ranks during the middle ages means at the time of feudal Japan.
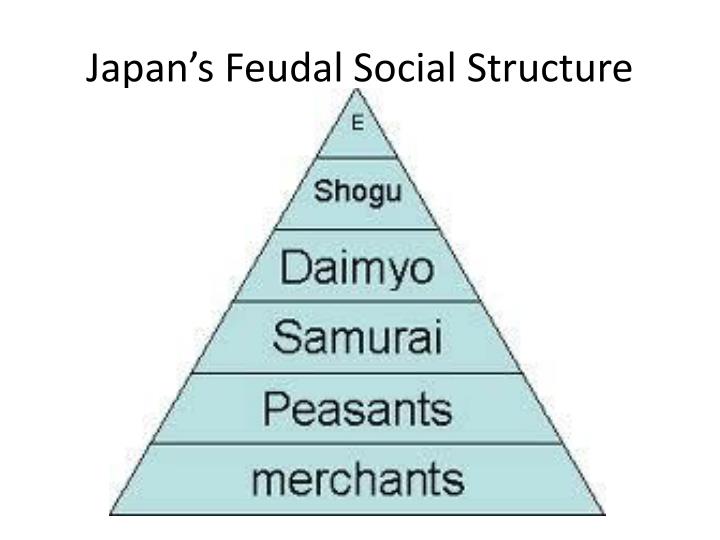
PPT Japanese Feudalism PowerPoint Presentation ID2941593
Origins & Structure. Feudalism (hoken seido), that is the arrangement between lords and vassals where the former gave favour or on (e.g. land, titles, or prestigious offices) in exchange for military service (giri) from the latter, began to be widespread in Japan from the beginning of the Kamakura Period (1185-1333).The main instigator was Minamoto no Yoritomo (1147-1199) who had established.

PPT Japan The land of the rising sun PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5457459
In probability samples of Japanese (N 1⁄4 1,027) and U.S. (N 1⁄4 1,805) adults, subjective social status more strongly predicted life satisfaction, positive affect, sense of purpose, and self-acceptance in the United States than in Japan.
The Hierarchy of Japan Japan Sakura no kuni
The Ancient Japanese Society possessed different Social Classes based on the Power and prestige. Ancient Japanese Hierarchy was majorly divided into two categories namely as the Noble Class and the Peasant Class.

Social Structures Medieval Japan 'Power and Perspective' LibGuides at Mount St Benedict College
Updated on July 08, 2019 Between the 12th and 19th centuries, feudal Japan had an elaborate four-tiered class system. Unlike European feudal society, in which the peasants (or serfs) were at the bottom, the Japanese feudal class structure placed merchants on the lowest rung.

Japanese Racial Hierarchy Japanese Social Structure
When it comes to feudal Japan social hierarchy, there are a lot of things that are significantly different from today's society in Japan and in the Western country. For example, merchants and artists in feudal japan were considered at the very bottom of the hierarchy. Feudal Japan social class distributions
Lesson 5 Japan International School History
Feudal Japanese society, which existed from the 12th to the mid-19th century, was based upon a ridge class system that determined each person's role. Similar to other elements of Japan at the time, the social structure was adopted from Chinese society, and had the same number of broad classes of people: four. Each of these classes are explained in more detail below.
hierarchy of Japanese feudal society Under The Shoguns
The JSEI and JSSI showed results similar to those found in European societies and so demonstrated their validity and usefulness for investigating social stratification in Japan, thereby extending European findings on social stratification into an Asian society. Issue Section: Articles Introduction
Chapter 2 Japan Under the Shoguns
Popular culture Contemporary Japanese society is decidedly urban. Not only do the vast majority of Japanese live in urban settings, but urban culture is transmitted throughout the country by a mass media largely concentrated in Tokyo.

Hierarchy Pyramid Japan under the Shogun
Follow the hierarchy order.. Business etiquette in Japan is highly influenced by social structure and culture, cultivating a very specific way of behaving during social interactions and business deals. Understanding the business culture do and don'ts in addition to Japanese body language, negotiations and ethics can help.

FileEdo social structure.svg Wikimedia Commons
Japanese people were assigned into a hierarchy of social classes based on the Four Occupations that were hereditary. The Emperor of Japan and the kuge were the official ruling class of Japan but had no power. The shōgun of the Tokugawa clan, the daimyō, and their retainers of the samurai class administered Japan through their system of domains.
Japanese Feudal Society Mr. Henson History
During the Edo (Tokugawa) period (1603-1867), there was a social division of the populace into four classes—warrior, farmer, craftsman, and merchant—with a peer class above and an outcast class below.